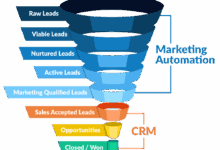
CRM Software for Small Business Success
CRM Software for Small Business: Unlocking growth isn’t just about selling more; it’s about nurturing lasting customer relationships. This guide explores how the right CRM system can streamline operations, enhance customer interactions, and ultimately boost your bottom line. We’ll delve into essential features, compare leading software options, and provide practical strategies for implementation and success.
From choosing the perfect software to integrating it seamlessly with your existing tools, we’ll cover every step of the journey. We’ll also look at how to measure your return on investment (ROI) and prepare for future trends in CRM technology. Whether you’re a retail store, a service provider, or an e-commerce business, this guide provides valuable insights to help you leverage the power of CRM for sustainable growth.
Defining Needs for Small Business CRM
Choosing the right CRM (Customer Relationship Management) software can significantly boost a small business’s efficiency and growth. A well-implemented CRM system streamlines operations, improves customer interactions, and ultimately contributes to increased profitability. Understanding your specific needs is crucial before selecting a system.
Effective CRM software helps small businesses centralize customer data, automate tasks, and improve communication, leading to better customer service and increased sales. The features prioritized will vary depending on the business type and its specific challenges.
Essential CRM Features for Small Businesses
Prioritizing essential features ensures a cost-effective and impactful CRM implementation. Overwhelmed by too many features can lead to underutilization and wasted resources. Focusing on the core needs allows for a smoother transition and quicker return on investment.
- Contact Management: A robust contact database allows for easy storage and retrieval of customer information, including contact details, purchase history, and communication logs. This facilitates personalized interactions and targeted marketing.
- Sales Pipeline Management: Tracking leads and opportunities through the sales process is crucial. Features like deal stages, probability tracking, and automated reminders help close deals faster and improve sales forecasting.
- Communication Tools: Integrated email, phone, and potentially even social media communication tools streamline interactions with customers. This centralized communication history provides a complete view of each customer’s journey.
- Reporting and Analytics: Understanding key metrics is vital. A CRM system should provide reports on sales performance, customer behavior, and marketing campaign effectiveness to inform strategic decisions.
- Task Management: Automating tasks like follow-ups, reminders, and scheduling frees up valuable time for more strategic activities, improving overall productivity.
CRM System Differences Across Small Business Types
The ideal CRM system varies significantly depending on the nature of the small business. Retail businesses have different needs than service-based businesses or e-commerce ventures. Understanding these differences is key to selecting the right fit.
- Retail: Retail CRMs often focus on point-of-sale (POS) integration, inventory management, and loyalty programs. They prioritize features that track customer purchases, preferences, and reward programs to enhance customer retention.
- Service-Based Businesses: Service businesses (e.g., consultants, plumbers) require CRMs with strong scheduling and appointment management capabilities. Tracking service calls, technician availability, and customer feedback are crucial for efficient operations.
- E-commerce: E-commerce CRMs integrate with online stores, track website activity, and manage online orders. Features like abandoned cart recovery, email marketing automation, and customer segmentation are highly valuable.
Solving Small Business Challenges with CRM Features
CRM systems directly address many common small business challenges. The right features can transform inefficient processes into streamlined workflows, leading to improved performance and profitability.
- Challenge: Losing track of leads. Solution: A CRM with lead management and pipeline tracking features helps visualize the sales process, ensuring no leads fall through the cracks. Automated reminders prevent follow-up delays.
- Challenge: Inconsistent customer communication. Solution: Integrated communication tools within a CRM centralize all customer interactions, providing a complete history and facilitating personalized communication.
- Challenge: Difficulty in understanding customer behavior. Solution: CRM reporting and analytics provide insights into customer purchasing patterns, preferences, and engagement levels, enabling data-driven decision-making.
- Challenge: Inefficient task management. Solution: CRM task automation and scheduling features free up time for employees to focus on higher-value activities, increasing overall productivity and reducing administrative burden.
Top CRM Software Options for Small Businesses
Choosing the right CRM software can significantly impact a small business’s efficiency and growth. This section compares three popular options, highlighting their strengths and weaknesses to help you make an informed decision. We’ll examine their pricing, user interfaces, and key features to guide your selection process.
Comparison of Three Popular CRM Systems
Three leading CRM systems frequently chosen by small businesses are HubSpot CRM, Zoho CRM, and Salesforce Essentials. Each offers a unique blend of features, pricing, and user experience, catering to different business needs and preferences. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the best fit.
User Interface and Ease of Use
The user interface (UI) significantly impacts a CRM’s usability. A user-friendly interface simplifies data entry, report generation, and overall system navigation, boosting productivity. HubSpot CRM is known for its intuitive and clean interface, making it easy for even non-technical users to navigate. Zoho CRM, while offering extensive features, can feel slightly more complex for beginners, requiring a steeper learning curve. Salesforce Essentials, while powerful, also presents a more complex interface compared to HubSpot, though its extensive customization options cater to specific business needs.
Key Features, Pricing, and Integrations
| Feature | HubSpot CRM | Zoho CRM | Salesforce Essentials |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pricing Model | Freemium (free plan with paid options) | Subscription-based (various plans) | Subscription-based (various plans) |
| Pricing (approx. monthly cost for basic plan) | Free (basic) to $450+ (for enterprise features) | $14 – $35+ (depending on users and features) | $25 – $100+ (depending on users and features) |
| Contact Management | Robust contact management with detailed profiles and interactions | Comprehensive contact management with custom fields and segmentation | Solid contact management with features for tracking interactions and managing relationships |
| Deal/Pipeline Management | Visual pipeline management for tracking sales progress | Visual pipeline management with customizable stages and workflows | Visual pipeline management with robust reporting and analytics |
| Reporting and Analytics | Basic reporting and analytics included in free plan, more advanced features in paid plans | Extensive reporting and analytics capabilities, including custom reports and dashboards | Advanced reporting and analytics tools to track key metrics and sales performance |
| Integrations | Integrates with various marketing and sales tools | Integrates with a wide range of apps and services via APIs and pre-built connectors | Integrates with various Salesforce ecosystem products and third-party apps |
| Ease of Use | Very user-friendly and intuitive | Moderate learning curve, more features can make it complex for beginners | Steeper learning curve, powerful but requires more time to master |
Implementation and Integration
Successfully implementing a CRM system requires careful planning and execution. A phased approach, focusing on clear objectives and user training, is crucial for a smooth transition and maximizing the return on investment. Ignoring these steps can lead to user resistance, data inconsistencies, and ultimately, failure to achieve the desired benefits from the new system.
Implementing a new CRM system within a small business involves several key steps. These steps should be approached methodically to ensure a successful transition and avoid disrupting daily operations. Effective communication throughout the process is also vital for gaining buy-in from employees and ensuring a smooth transition.
CRM System Implementation Steps
A well-defined implementation plan is essential. This plan should outline specific tasks, timelines, and responsibilities for each team member. Clear communication and regular progress updates are key to staying on track. The following steps provide a framework for a successful implementation:
- Data Cleansing and Migration: Before importing data, clean and standardize existing customer data to ensure accuracy and consistency. This involves identifying and correcting errors, duplicates, and inconsistencies.
- System Configuration: Configure the CRM system to match the specific needs and workflows of the business. This includes customizing fields, creating workflows, and setting up user roles and permissions.
- User Training and Onboarding: Provide comprehensive training to all users on how to effectively use the new CRM system. This includes hands-on training and ongoing support.
- Initial Data Import: Import the cleaned and standardized data into the new CRM system. Regularly check for data integrity and make corrections as needed.
- Testing and Refinement: Thoroughly test the system to identify and resolve any issues before full deployment. Make necessary adjustments based on feedback from users.
- Go-Live and Ongoing Support: Launch the CRM system and provide ongoing support to users. Monitor system performance and make adjustments as needed.
Data Migration Challenges and Best Practices
Data migration is a critical step, often fraught with challenges. Inaccurate or incomplete data can significantly hinder the effectiveness of the CRM system. Careful planning and execution are vital to minimize disruptions and ensure data integrity.
- Data Cleansing: Identifying and correcting errors, inconsistencies, and duplicates in existing data is crucial. This often involves manual review and data standardization.
- Data Mapping: Carefully map the fields in the existing system to the corresponding fields in the new CRM system. This ensures accurate data transfer and avoids data loss.
- Data Validation: Validate the migrated data to ensure accuracy and completeness. This may involve comparing the data in the new system to the original data source.
- Incremental Migration: Consider a phased approach to data migration, starting with a small subset of data to test the process and identify any issues before migrating the entire dataset.
- Data Backup: Always back up the existing data before initiating the migration process. This provides a safety net in case of unexpected issues.
CRM Integration with Other Business Tools
Integrating the CRM system with other business tools, such as email marketing platforms and accounting software, can significantly enhance efficiency and streamline workflows. This integration often involves using APIs or third-party integration tools.
For example, integrating with an email marketing platform allows for automated email campaigns based on customer interactions within the CRM. Integration with accounting software can automate invoicing and payment processing, providing a complete view of customer interactions and financial transactions. Proper integration can significantly reduce manual data entry and improve overall data accuracy. This reduces the risk of errors and improves the overall efficiency of business operations.
Training and Support
Successful CRM implementation hinges on effective training and readily available support. Employees need to understand the software’s functionality to utilize it properly, maximizing its benefits for the business. Equally crucial is a robust support system to address any challenges or questions that arise during and after the implementation process.
A well-structured training program and responsive support system are key to a smooth transition and ongoing success with your new CRM. This ensures employees feel confident and empowered to use the software effectively, ultimately improving customer relationships and boosting overall business efficiency.
Sample Training Program for Employees
This sample program outlines a phased approach to CRM training, catering to different learning styles and paces. The program incorporates both theoretical knowledge and hands-on practice to ensure comprehensive understanding and competency.
- Module 1: Introduction to the CRM System (1 hour): Overview of the CRM software, its purpose, and key features. This includes a demonstration of the user interface and navigation. A brief quiz follows to assess initial understanding.
- Module 2: Contact Management (2 hours): Detailed explanation of adding, editing, and managing contacts within the system. This includes importing existing contacts and utilizing advanced search and filtering options. Hands-on exercises are incorporated to reinforce learning.
- Module 3: Lead Management (2 hours): Focuses on the process of identifying, qualifying, and nurturing leads. This includes using the CRM’s lead scoring and tracking features. A simulated lead management scenario is used for practical application.
- Module 4: Sales Process Management (2 hours): Covers managing sales opportunities, tracking deals, and forecasting sales. This includes using the CRM’s reporting and analytics tools to monitor progress. A case study illustrating a successful sales cycle is presented.
- Module 5: Reporting and Analytics (1 hour): Focuses on interpreting data and generating reports to track key performance indicators (KPIs). This includes customizing reports and dashboards to meet specific business needs. Practical exercises involve creating and analyzing sample reports.
- Module 6: Advanced Features (2 hours): Exploration of advanced features such as automation, integration with other tools, and customization options. This allows employees to optimize their workflow and leverage the full potential of the CRM. Open Q&A session concludes the module.
Essential Elements of Effective CRM Customer Support
Effective CRM customer support should be readily available, comprehensive, and user-friendly. Proactive support, addressing potential issues before they arise, is also crucial.
- Multiple Support Channels: Offering support via phone, email, and live chat ensures accessibility for all employees.
- Knowledgeable Support Staff: Support personnel should possess in-depth knowledge of the CRM software and be capable of resolving a wide range of issues.
- Quick Response Times: Prompt responses to inquiries are vital to minimize disruption and maintain employee productivity.
- Comprehensive Documentation: Detailed user manuals, tutorials, and FAQs should be readily available.
- Regular Updates and Training: Ongoing support includes regular updates to address bugs and introduce new features, along with refresher training sessions.
Resources for Employees
Providing employees with readily accessible resources is crucial for efficient CRM adoption and ongoing success. These resources should be well-organized and easily searchable.
- Comprehensive User Manual: A detailed guide covering all aspects of the CRM software, including screenshots and step-by-step instructions.
- Video Tutorials: Short, focused videos demonstrating key functionalities and workflows.
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs): A searchable database addressing common questions and issues encountered by users.
- Online Help Center: A centralized online resource providing access to all documentation, tutorials, and FAQs.
- Internal CRM Support Team Contact Information: Clear contact information for the internal support team, specifying available communication channels and response times.
Measuring ROI and Success
Implementing a CRM system is an investment, and like any investment, you need to understand its return. Measuring the ROI of your CRM software involves tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) and analyzing the data to demonstrate its impact on your business. This process goes beyond simply noting an increase in sales; it’s about understanding *how* the CRM contributed to that growth and identifying areas for further optimization.
Tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) provides quantifiable evidence of your CRM’s effectiveness. By monitoring these metrics, you can pinpoint areas of strength and weakness, justifying the ongoing investment and informing future strategic decisions. A proactive approach to KPI tracking ensures your CRM remains a valuable asset, continually improving efficiency and driving revenue growth.
Key Performance Indicators for CRM Success
Several crucial KPIs can be tracked to assess the effectiveness of your CRM software. These metrics provide a holistic view of its impact across various business functions, allowing for a comprehensive ROI assessment. Careful selection and consistent monitoring of these KPIs are essential for effective measurement.
- Lead Conversion Rate: This metric measures the percentage of leads that convert into paying customers. A higher conversion rate indicates improved lead nurturing and sales processes facilitated by the CRM.
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): This shows the cost of acquiring a new customer. A decrease in CAC demonstrates the CRM’s efficiency in streamlining the sales process and reducing marketing expenses.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV): This metric represents the total revenue generated by a customer throughout their relationship with your business. An increase in CLTV highlights the CRM’s role in fostering customer loyalty and retention.
- Sales Cycle Length: This measures the time it takes to close a deal. A shorter sales cycle indicates improved efficiency in lead management and sales processes.
- Customer Churn Rate: This shows the percentage of customers who stop doing business with your company. A lower churn rate indicates improved customer satisfaction and retention strategies supported by the CRM.
- Average Revenue Per User (ARPU): This KPI shows the average revenue generated per customer. An increase in ARPU demonstrates successful upselling or cross-selling initiatives enabled by the CRM’s customer data insights.
Using CRM Data to Improve Business Operations
The data collected within your CRM system is a powerful tool for improving various aspects of your business. By analyzing this data, you can identify trends, predict future outcomes, and make data-driven decisions to optimize operations and boost profitability. This proactive approach transforms the CRM from a simple contact management system into a strategic business asset.
Examples of CRM Reports for ROI Demonstration
The ability to generate insightful reports is a key benefit of CRM software. These reports provide visual representations of your KPIs, allowing for easy identification of trends and successes. Presenting these reports to stakeholders demonstrates the tangible return on investment of the CRM system.
- Sales Performance Report: This report visualizes sales figures over a specific period, showing trends in revenue, conversion rates, and sales cycle length. It could include charts comparing performance before and after CRM implementation.
- Customer Satisfaction Report: This report tracks customer feedback, satisfaction scores, and support ticket resolution times. Improvements in these metrics demonstrate the CRM’s positive impact on customer relationships.
- Marketing Campaign ROI Report: This report analyzes the effectiveness of marketing campaigns by tracking lead generation, conversion rates, and cost per acquisition. It shows the direct contribution of the CRM to marketing campaign success.
- Lead Source Report: This report identifies the most effective sources of leads, helping to optimize marketing efforts and improve lead generation strategies. It might illustrate a shift towards higher-quality leads post-CRM implementation.
For example, a company might show a 20% increase in lead conversion rates and a 15% reduction in customer acquisition costs after implementing a CRM, directly translating to a significant increase in profitability. Another company might demonstrate a decrease in customer churn rate from 10% to 5%, illustrating the CRM’s effectiveness in improving customer retention and increasing customer lifetime value. These tangible results, clearly presented in reports, effectively showcase the ROI of the CRM investment.
Future Trends in Small Business CRM
The landscape of Customer Relationship Management (CRM) is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and changing business needs. Small businesses, often operating with limited resources, need to understand these emerging trends to remain competitive and leverage CRM effectively for growth. Failing to adapt could mean missing out on valuable opportunities for improved customer engagement and operational efficiency.
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and automation is rapidly transforming CRM software, offering small businesses unprecedented capabilities. This evolution presents both opportunities and challenges, requiring proactive adaptation to maximize benefits and mitigate potential risks.
AI-Powered CRM Features and Their Impact
AI is enhancing CRM in several key areas. Predictive analytics, powered by machine learning algorithms, can forecast customer behavior, identify potential churn risks, and personalize marketing efforts. For example, a small bakery using a CRM with predictive analytics could anticipate increased demand around holidays and proactively adjust staffing and inventory. Chatbots, another AI-driven feature, can handle routine customer inquiries, freeing up human employees to focus on more complex tasks and higher-value interactions. Automated workflows streamline processes like lead nurturing and follow-up, improving efficiency and reducing manual effort. These advancements allow small businesses to operate more efficiently and provide better customer service with fewer resources.
The Rise of Mobile-First CRM
Access to CRM data and functionality is increasingly shifting to mobile devices. Mobile-first CRM solutions are designed for intuitive use on smartphones and tablets, enabling employees to access customer information and manage interactions from anywhere. This is crucial for small businesses with field-based employees, such as sales representatives or service technicians, who need real-time access to customer data. Imagine a plumber using a mobile CRM to access customer details, service history, and scheduling information directly on their tablet while on a job site. This immediacy improves responsiveness and customer satisfaction.
Integration with Other Business Tools
The future of CRM lies in seamless integration with other essential business tools. Small businesses are increasingly relying on a variety of software solutions for various functions, such as accounting, marketing automation, and e-commerce. CRM platforms that offer robust integration capabilities allow for a centralized view of customer data and streamlined workflows across different departments. This unified approach reduces data silos, eliminates manual data entry, and enhances overall business efficiency. A small online retailer, for example, can integrate their CRM with their e-commerce platform to track customer purchases, interactions, and preferences, leading to more targeted marketing campaigns and improved customer loyalty.
Preparing for Future CRM Trends
Small businesses can prepare for these trends by:
- Regularly evaluating their current CRM system and its capabilities.
- Researching and selecting CRM solutions with AI and automation features.
- Prioritizing mobile accessibility in their CRM selection process.
- Focusing on CRM solutions that offer robust integration with other business tools.
- Investing in employee training to effectively utilize the advanced features of their CRM system.
By adopting a proactive approach and embracing these technological advancements, small businesses can unlock the full potential of CRM and gain a competitive edge in the marketplace.
Illustrative Examples of CRM Use Cases
Understanding how CRM software functions in real-world scenarios is crucial for appreciating its value. The following examples showcase the diverse applications of CRM across different small business models, highlighting the benefits of improved customer relationships and operational efficiency.
Retail Business: Enhancing Customer Loyalty with CRM
A small boutique clothing store, “Threads,” uses a CRM system to track customer purchases, preferences, and interactions. When a customer, Sarah, buys a specific style of dress, the CRM automatically records this information, including her size and preferred color. On Sarah’s birthday, the CRM triggers a personalized email offering a discount on similar dresses or accessories. Furthermore, when Sarah returns to the store, the staff, accessing her profile through the CRM, can greet her by name and offer tailored recommendations, creating a personalized shopping experience. The CRM also allows Threads to segment customers based on purchasing history, enabling targeted marketing campaigns for specific product lines or seasonal sales. This personalized approach fosters customer loyalty and drives repeat business. Analyzing purchase patterns within the CRM allows Threads to optimize inventory and predict future demand, improving efficiency and reducing waste.
Service-Based Business: Managing Appointments, Projects, and Client Follow-Up
“Fix-It Fast,” a small handyman service, utilizes CRM to streamline its operations. The CRM’s calendar function allows clients to book appointments online, which are automatically synced with the technicians’ schedules, preventing double-bookings. Each project is created as a record in the CRM, detailing the client’s information, the services rendered, the materials used, and the project timeline. Automated email reminders are sent to clients before appointments and after project completion. The CRM tracks all communication with clients, ensuring consistent follow-up and facilitating efficient project management. For instance, if a client has questions after a job is finished, all previous communication is readily accessible, allowing the technician to quickly address their concerns. This comprehensive tracking enables Fix-It Fast to improve service delivery and maintain strong client relationships.
E-commerce Business: Personalizing Marketing and Improving Customer Segmentation
“Eco-Friendly Goods,” an online store selling sustainable products, uses its CRM to segment its customer base. The CRM collects data on customer purchases, browsing history, and email engagement. This data is used to create customer segments based on interests (e.g., organic food, reusable products, ethical fashion). Targeted email marketing campaigns are then launched, offering personalized product recommendations and promotions to each segment. For example, customers who frequently purchase organic food receive emails highlighting new organic products and recipes. The CRM also analyzes website traffic and purchase data to identify potential churn risks. Proactive email campaigns, offering discounts or loyalty programs, are then sent to these customers to encourage repeat business. This personalized approach improves customer engagement and increases sales conversion rates. The CRM also tracks the success of each campaign, providing valuable insights for future marketing strategies.
Final Wrap-Up
Implementing a CRM system is an investment in your small business’s future. By carefully selecting the right software, integrating it effectively, and consistently tracking key performance indicators (KPIs), you can transform your customer relationships, improve efficiency, and achieve significant growth. Remember that ongoing training and adaptation are crucial for maximizing the benefits of your CRM system. Embrace the possibilities, and watch your business flourish.